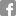3D Deformable Partial Shape Matching
Description
The datasets we provide here can be used for tasks of deformable 3D shape matching and retrieval under partiality transformations. This is considered a more challenging setting if compared to the more classical tasks dealing with full shapes.
There are two datasets, named cuts (456 partial shapes) and holes (684 partial shapes), exemplifying different kinds of partiality. The shapes span different classes and are based on the TOSCA high-resolution dataset. The cuts dataset consists of shapes undergoing a single cut; an example is given by the human on the left, above. The holes dataset is more challenging, as it contains irregular holes and multiple cuts; see the middle and right examples above.
In addition to the partial shapes we provide null shapes for each class, i.e. full shapes in a canonical pose. These can be used to perform part-to-whole matching, as we did in the paper below. The null shapes are the same as the originals from TOSCA, remeshed to 10K vertices for additional challenge. All partial shapes are also remeshed.
Format
For the holes dataset, the filenames contain information on how the partial shape was produced. For example, cat3_A0.70_H25 means that approximately 70% of the total area was eroded from the full shape of cat3, starting from 25 equally distributed seeds. We refer to the paper below for additional details.
For each shape in the two datasets, we provide:
- the mesh file
- the ground-truth matches towards the original high-resolution null shape from TOSCA
- the index mapping from the high-resolution mesh to the remeshed version
Download
You can download the dataset in three different formats. Each archive also contains a selected folder with the shapes that were used for the experiments in the paper below. You can use the selected shapes for direct comparisons.
Note: All triangle indices start from 1 (Matlab style).
OFF or ASCII or Matlab (300MB each)
We also provide some demo code implementing our method; it reproduces Figure 9 from the paper. Note: This code is only for demonstration purposes and it is not in its final version; in particular, it should not be used for comparisons. The final code will be made available as soon as possible. You are welcome to contact the authors for updates.
Reference
Please refer to the following paper if you use the dataset:
Partial Functional Correspondence
E. Rodola, L. Cosmo, M. M. Bronstein, A. Torsello, and D. Cremers
In Computer Graphics Forum (to appear)